Email cannot be empty
Password cannot be empty
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent

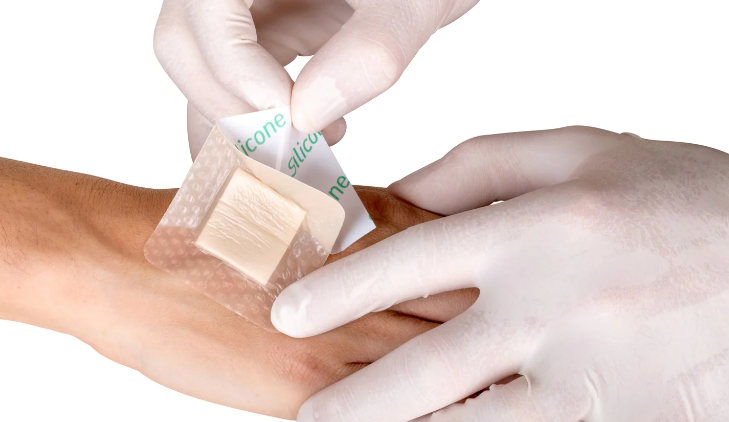
The Ultimate Guide to Foam Dressings for Wound Care: What You Need to Know
Wound care is an essential part of healing, and while it might not sound like the most glamorous topic, it is crucial for everyone to understand. Whether you've got a scraped knee, a surgical incision, or a more chronic condition like a diabetic ulcer, choosing the right dressing can make all the difference in how quickly and effectively your wound heals. One of the most effective and widely used options is the foam dressing.
In this blog, we'll explore everything you need to know about foam dressing for wound care, from what it is, to how it works, and why it could be the best option for your needs. We'll also dive into the different types of foam dressings, their benefits, and tips on how to use them properly. So, let’s break it down step by step and get to know this highly useful wound care tool!
What is a Foam Dressing?
Foam dressings are made from a soft, absorbent material that provides a moist environment for the wound to heal while protecting it from external contaminants, bacteria, and damage. The foam is often designed with several layers, including an absorbent core that draws excess moisture away from the wound. They are typically breathable but offer a barrier against dirt and bacteria, which makes them ideal for managing wounds that produce moderate to heavy amounts of exudate (wound fluid).
These dressings come in various sizes and shapes, which makes them adaptable to different kinds of wounds, whether they're large, small, deep, or shallow. Additionally, some foam dressings come with adhesive borders to hold the dressing in place, while others are non-adhesive, making them more versatile for delicate or sensitive skin.
How Does Foam Dressing Work?
One of the primary roles of a foam dressing is to maintain the right balance of moisture at the wound site. This is important because wounds need to stay moist in order to heal efficiently, but too much moisture can lead to maceration, where the skin around the wound becomes soft and breaks down.
Here's how foam dressings help:
Absorption of Exudate: Foam dressings are highly absorbent, making them ideal for wounds that are producing a lot of exudate. The foam pulls away this moisture while keeping the wound bed adequately hydrated.
Cushioning and Protection: Foam provides a cushion between the wound and external factors like pressure, clothing, or accidental bumps. This cushioning can be especially beneficial for pressure ulcers or wounds in high-friction areas.
Bacterial Barrier: The outer layer of many foam dressings acts as a barrier against harmful bacteria and environmental contaminants, helping to reduce the risk of infection.
Breathability: Foam dressings are designed to be semi-permeable, allowing oxygen to reach the wound while allowing moisture vapor to escape. This promotes better healing and helps prevent excess moisture buildup.
Types of Foam Dressings
Foam dressings are available in different forms to cater to specific types of wounds. Here are some of the most common types:
1. Adhesive Foam Dressings
These foam dressings come with a built-in adhesive border, which helps the dressing stay in place without the need for extra tape or bandages. Adhesive foam dressings are convenient and easy to apply, but may not be suitable for people with sensitive skin, as the adhesive could cause irritation.
2. Non-Adhesive Foam Dressings
Non-adhesive foam dressings are a great option for people with sensitive or fragile skin. Since they don't have an adhesive border, they are usually secured with an additional bandage or tape. Non-adhesive options are often used for wounds that require frequent dressing changes or for skin that may be damaged by adhesives.
3. Silicone Foam Dressings
Silicone foam dressings have a soft silicone layer that gently adheres to the skin, which makes them less likely to cause trauma during dressing changes. These are especially useful for people with fragile or sensitive skin, as they reduce pain and discomfort during removal.
4. Antimicrobial Foam Dressings
Some foam dressings are treated with antimicrobial agents, such as silver, to help reduce the risk of infection in wounds that are at higher risk of contamination. These dressings are great for wounds that show signs of infection or for patients who are at higher risk due to conditions like diabetes.
5. Hydrophilic Foam Dressings
Hydrophilic foam dressings are designed to absorb large amounts of exudate quickly. This makes them ideal for very wet wounds that need to be kept clean and dry. They are particularly beneficial for heavily draining wounds like venous leg ulcers or post-surgical wounds.
Benefits of Foam Dressings for Wound Care
So, why are foam dressings such a popular choice for wound care? Here are some of their key benefits:
1. High Absorbency
Foam dressings can absorb a significant amount of exudate, making them ideal for wounds that produce a lot of fluid. By keeping the wound dry, foam dressings help prevent maceration and keep the wound bed healthy.
2. Moist Wound Healing Environment
One of the key factors in wound healing is moisture balance. Foam dressings maintain an optimal moisture level, which helps skin cells regenerate more quickly. This also minimizes scab formation, allowing for faster healing with less risk of scarring.
3. Pain Reduction
Because foam dressings are soft and cushiony, they can help reduce pain by protecting the wound from pressure, friction, and further trauma. The material is gentle on the skin, and some types, like silicone foam dressings, are specifically designed to minimize pain during dressing changes.
4. Long Wear Time
Foam dressings can be worn for extended periods, depending on the amount of exudate the wound produces. This means fewer dressing changes, which can make wound management easier for both the patient and caregiver. It also reduces the potential for infection since the dressing doesn't need to be disturbed as often.
5. Versatility
Foam dressings can be used on a wide range of wound types, from minor abrasions and burns to more severe wounds like pressure ulcers and post-surgical incisions. Their adaptability makes them an excellent choice for various clinical situations.
6. Bacterial Barrier
The top layer of foam dressings often acts as a barrier against bacteria and external contaminants, which helps reduce the risk of infection. This is especially important for wounds that are slow to heal or for individuals who are immunocompromised.
When to Use Foam Dressings
While foam dressings are highly versatile, they are particularly beneficial for certain types of wounds. Here are some situations where foam dressing for wound care is especially useful:
Pressure ulcers: Foam dressings can help protect pressure ulcers from further trauma and absorb the exudate that typically accompanies these types of wounds.
Post-surgical wounds: After surgery, keeping a wound clean, dry, and protected is essential. Foam dressings can offer that protection while also allowing for the wound to stay moist enough to heal properly.
Diabetic ulcers: People with diabetes often experience slow-healing ulcers, particularly on their feet. Foam dressings can help manage the moisture levels and protect the wound from bacteria, which is crucial for preventing further complications.
Burns and abrasions: Foam dressings are also useful for shallow wounds like burns and abrasions that require a moist environment to heal properly.
How to Apply Foam Dressings
Applying foam dressings correctly is crucial for ensuring the best healing outcomes. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
Clean the Wound: Before applying any dressing, it's important to clean the wound using a saline solution or an appropriate wound cleanser. This helps to remove debris and reduce the risk of infection.
Dry the Surrounding Skin: While the wound itself needs to stay moist, the surrounding skin should be dry to prevent maceration. Use a clean cloth or gauze to gently pat the area dry.
Select the Right Size: Choose a foam dressing that is large enough to cover the entire wound and extend about an inch beyond its edges. This ensures that the dressing stays in place and provides adequate protection.
Apply the Dressing: Place the foam dressing over the wound, making sure the absorbent side is facing the wound bed. If you’re using an adhesive foam dressing, press down gently on the edges to secure it. For non-adhesive dressings, use tape or a bandage to keep it in place.
Monitor and Change as Needed: Check the dressing regularly for signs of excessive exudate or saturation. Depending on the wound type and dressing used, foam dressings can typically be left in place for several days before needing to be changed.
Conclusion
Foam dressing for wound care is a powerful and versatile tool in modern medicine. Its ability to absorb excess fluid, maintain a moist healing environment, and protect wounds from infection makes it a top choice for a wide range of wound types. Whether you're dealing with a chronic condition like a diabetic ulcer or a simple scrape, foam dressings offer a convenient, effective, and comfortable solution.
By understanding the different types of foam dressings, their benefits, and how to use them properly, you can take control of wound care and ensure that your injuries heal as quickly and comfortably as possible.

